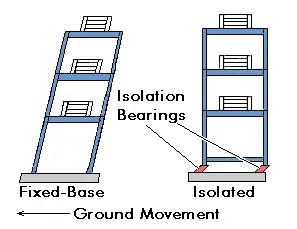
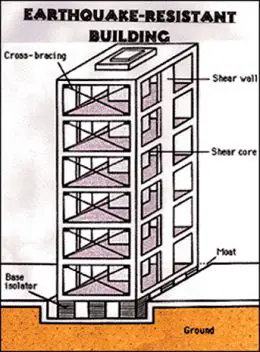
The aim of earthquake resistant building design is to prevent total collapse of building structures.
- It saves human lives.
- It relies on ductility (ability to deform inelastically) and redundancy (many load path).
The aim of earthquake proof building design is also to control structural and nonstructural damage in structures.
- It minimizes economic loss in not so severe earthquakes.
- Earthquake forces have great uncertainty and it is uneconomic and infeasible to design for no damage.
Four Steps Approach To Earthquake Resistant Building Design
The earthquake resistant building design generally include 4 steps as follows.
- Sound initial planning: Layout, plan and structural form.
- Appropriate analysis and design
- Proper detailing of structural and nonstructural components.
- Quality control in design and construction.
Planning Considerations of Design
1. Site Conditions
- Liquefaction
- Stability of slopes
- Site period
2. Geometrically Sample Forms
- Uniformity and regularity is highly desirable in earthquake resistant building design.
- Avoid concentration of mass especially near the top (massive roofs).
3. Symmetrical and Compact Plan Forms
- Square or rectangular footprint is desirable.
- No complex L, T, or U plans.
4. Enough clearance between adjacent buildings.
5. Enough redundancy: Backup elements.