Vacuum Evaporation
Vacuum evaporation is when the pressure in a container filled with liquid is reduced below the vapor pressure of the liquid. This causes the liquid to evaporate at a lower temperature than normal. The vapors are almost completely removed other than the source material before the process begins.
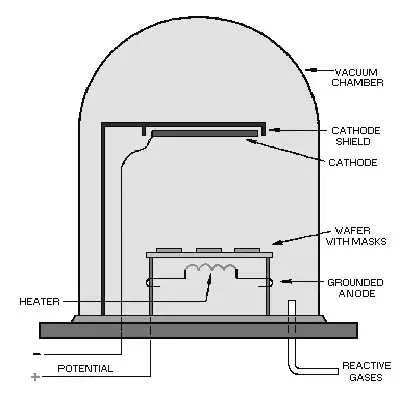
Some Vacuum Evaporation Facts
Here are 8 vacuum evaporation facts you should know.
- Evaporation involves two basic processes. A hot source material will evaporate and condenses on the substrate. The gaseous environment and heat source of vacuum evaporation is different from the familiar process of water evaporating from a boiling pot.
- The evaporation takes place within a vacuum. The vapors are almost completely removed before the process even begins.
- Atoms that have evaporated can collide with foreign particles and have the potential to react with them. These evaporated atoms reduce the amount of vapor that will reach the substrate. This makes it difficult to control the thickness.
- Materials that evaporate will deposit non-uniformly if the substrate has a rough surface.
- Evaporated material attacks the substrate from a mostly single direction causing protruding features to block the evaporated material from some areas; this is called step coverage or shadowing.
- When the vacuum is poor and close to the atmospheric pressure, the deposition is usually non-uniform and tends to not have a smooth or continuous film. The deposition will appear fuzzy.
- In a high vacuum, the evaporated particles can travel directly to the deposition target and not collide with any of the background gases.
- Any hot objects within the evaporation chamber, like heating filaments, will produce unwanted vapors that will limit the quality of the vacuum.

